I accidentally deleted a folder on my external WD Thunderbolt Duo drive. What are the chances of recovering the data?
Data Loss on External Drives: Causes and Precautionary Measures
When it comes to external drives, it is crucial to understand the primary causes of data loss. Here are the key factors that can lead to data loss:
- Accidental or intentional data deletion by the user or due to software failure.
- File system failure or corruption of the file allocation table, rendering data inaccessible.
- Hardware issues with the drive, such as physical damage, leading to failures in reading data.
Immediate Actions to Take After Data Loss on an External Drive
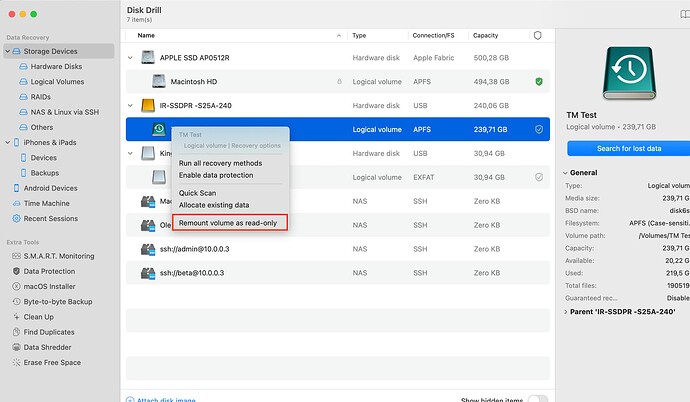
If you realize that data on an external drive has been lost, the first step should be to stop using the drive. Continuing to use it may result in overwriting the lost data since the system may continue writing data to the drive. To minimize the risk of further loss, it is crucial to immediately unmount the partition with the data or switch the drive to read-only mode.
Use specialized software, such as Disk Drill, to switch the external drive to read-only mode. This will help prevent any further modifications to the drive, preserving the chances of successful data recovery.
Assessing the Likelihood of Data Recovery
Not all data loss situations are the same. Sometimes recovery is possible with minimal effort, while in other cases, complex procedures may be required. The success of data recovery on an external drive depends on various factors, including the state of the device and the actions taken immediately after data loss.
External Drives with SMR Technology
Drives using SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording) technology are often used as external storage due to their high capacity and affordable price. However, this technology has certain characteristics that can complicate the data recovery process:
- Capacity: SMR drives are often found in capacities ranging from 1 TB to 8 TB.
- Form Factor: These are usually 3.5-inch drives used in desktop computers, as well as 2.5-inch models for laptops and external drives.
- Types of Devices: SMR drives are used in budget models of hard drives for archival data storage, backups, and in NAS systems.
The Impact of TRIM on Data Recovery from External Drives
The TRIM command plays an important role in managing data on SSDs and SMR HDDs, but it can also complicate data recovery. Once the TRIM command is executed, the data on the external drive may be irreversibly deleted, making recovery virtually impossible. It is important to note that TRIM works differently under Windows and macOS, and its impact varies depending on the file system and type of drive.
SMART and Its Impact on Data Recovery from External Drives
SMART technology helps predict potential drive failures. Key parameters such as Reallocated Sectors Count and Current Pending Sector Count can indicate issues with the drive, reducing the likelihood of successful data recovery. Among the popular tools for diagnosing SMART data are CrystalDiskInfo, DriveDX, and Disk Drill.
Preparing for Data Recovery
Before starting the recovery process, it is recommended to create a byte-to-byte backup of the data on the external drive. This will protect the original data from further damage and allow you to work with a copy without risk. To scan the image or drive, use specialized software like Disk Drill to maximize the chances of successful data recovery.
The final step involves comparing the scan results using different programs, which will help you choose the best recovery method.
Conclusion
So, the best chances for recovering lost data from external drives are in the following cases:
- Windows: Recovery is most successful on CMR HDDs with any file system, SMR HDDs with exFAT or FAT file systems, and SSDs with exFAT or FAT.
- macOS: Data recovery is most likely on any USB HDD or SSD, provided that TRIM support is not forcibly enabled.
The most challenging cases for data recovery include:
- Windows: SMR HDDs or SSDs with NTFS or ReFS file systems.
- macOS: Thunderbolt SSDs or SMR HDDs with HFS+ or APFS file systems.
These guidelines will help you assess the chances of successful data recovery depending on the device and operating system in use. It is essential to remember that taking the right actions immediately after data loss significantly increases the likelihood of successful recovery.
If the data is highly valuable, it is advisable to seek professional help immediately. You can use services from specialists, for example, through Datarecovery.net.